跨域方法总结
最近面试问的挺多的一个问题,就是JavaScript的跨域问题。在这里,对跨域的一些方法做个总结。由于浏览器的同源策略,不同域名、不同端口、不同协议都会构成跨域;但在实际的业务中,很多场景需要进行跨域传递信息,这样就催生出多种跨域方法。
1. 具备src的标签
- 原理:所有具有
src属性的HTML标签都是可以跨域的
在浏览器中,<script>、<img>、<iframe>和<link>这几个标签是可以加载跨域(非同源)的资源的,并且加载的方式其实相当于一次普通的GET请求,唯一不同的是,为了安全起见,浏览器不允许这种方式下对加载到的资源的读写操作,而只能使用标签本身应当具备的能力(比如脚本执行、样式应用等等)。
2. JSONP跨域
- 原理:
<script>是可以跨域的,而且在跨域脚本中可以直接回调当前脚本的函数
script标签是可以加载异域的JavaScript并执行的,通过预先设定好的callback函数来实现和母页面的交互。它有一个大名,叫做JSONP跨域,JSONP是JSON with Padding的略称。它是一个非官方的协议,明明是加载script,为啥和JSON扯上关系呢?原来就是这个callback函数,对它的使用有一个典型的方式,就是通过JSON来传参,即将JSON数据填充进回调函数,这就是JSONP的JSON+Padding的含义。JSONP只支持GET请求。
前端代码:
<script type="text/javascript">
function dosomething(jsondata){
//处理获得的json数据
}
</script>
<script src="http://haorooms.com/data.php?callback=dosomething"></script>后台代码:
<?php
$callback = $_GET['callback'];//得到回调函数名
$data = array('a','b','c');//要返回的数据
echo $callback.'('.json_encode($data).')';//输出
?>3. 跨域资源共享(CORS)
- 原理:服务器设置Access-Control-Allow-Origin HTTP响应头之后,浏览器将会允许跨域请求
CORS是HTML5标准提出的跨域资源共享(Cross Origin Resource Share),支持GET、POST等所有HTTP请求。CORS需要服务器端设置Access-Control-Allow-Origin头,否则浏览器会因为安全策略拦截返回的信息。
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * # 允许所有域名访问,或者
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://a.com # 只允许所有域名访问CORS又分为简单跨域和非简单跨域请求,有关CORS的详细介绍请看阮一峰的跨域资源共享 CORS 详解,里面讲解的非常详细。
4. document.domain
- 原理:相同主域名不同子域名下的页面,可以设置document.domain让它们同域
我们只需要在跨域的两个页面中设置document.domain就可以了。修改document.domain的方法只适用于不同子域的框架间的交互,要载入iframe页面。
例如:1. 在页面 http://a.example.com/a.html 设置document.domain
<iframe id = "iframe" src="http://b.example.com/b.html" onload = "test()"></iframe>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.domain = 'example.com';//设置成主域
function test(){
alert(document.getElementById('iframe').contentWindow);//contentWindow 可取得子窗口的 window 对象
}
</script>2、在页面http:// b.example.com/b.html 中设置document.domain
<script type="text/javascript">
document.domain = 'example.com';//在iframe载入这个页面也设置document.domain,使之与主页面的document.domain相同
</script>5. window.name
- 原理:window对象有个name属性,该属性有个特征:即在一个窗口(window)的生命周期内,窗口载入的所有的页面都是共享一个window.name的,每个页面对window.name都有读写的权限,window.name是持久存在一个窗口载入过的所有页面中的。
这里有三个页面:
- sever.com/a.html 数据存放页面
- agent.com/b.html 数据获取页面
- agent.com/c.html 空页面,做代理使用
a.html中,设定window.name作为需要传递的值
<script>
window.name = 'I was there!';
alert(window.name);
</script>b.html中,当iframe加载后将iframe的src指向同域的c.html,这样就可以利用iframe.contentWindow.name获取要传递的值了
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
iframe = document.createElement('iframe');
iframe.style.display = 'none';
var state = 0;
iframe.onload = function() {
if(state === 1) {
var data = JSON.parse(iframe.contentWindow.name);
alert(data);
iframe.contentWindow.document.write('');
iframe.contentWindow.close();
document.body.removeChild(iframe);
} else if(state === 0) {
state = 1;
iframe.contentWindow.location = 'http://agent.com/c.html';
}
};
iframe.src = 'http://sever.com/a.html';
document.body.appendChild(iframe);
</script>
</body>6. window.postMesage
- 原理: HTML5新增的postMessage方法,通过postMessage来传递信息,对方可以通过监听message事件来监听信息。可跨主域名及双向跨域。
这里有两个页面:
- agent.com/index.html
- server.com/remote.html
本地代码index.html
<body>
<iframe id="proxy" src="http://server.com/remote.html" onload = "postMsg()" style="display: none" ></iframe>
<script type="text/javascript">
var obj = {
msg: 'hello world'
}
function postMsg (){
var iframe = document.getElementById('proxy');
var win = iframe.contentWindow;
win.postMessage(obj,'http://server.com');
}
</script>
</body>postMessage的使用方法: otherWindow.postMessage(message, targetOrigin);
- otherWindow: 指目标窗口,也就是给哪个window发消息,是 window.frames 属性的成员或者由 window.open 方法创建的窗口
- message: 是要发送的消息,类型为 String、Object (IE8、9 不支持)
- targetOrigin: 是限定消息接收范围,不限制请使用 ‘*’
server.com上remote.html,监听message事件,并检查来源是否是要通信的域。
<head>
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onmessage = function(e){
if(e.origin !== 'http://localhost:8088') return;
alert(e.data.msg+" from "+e.origin);
}
</script>
</head>7. location.hash
原理:
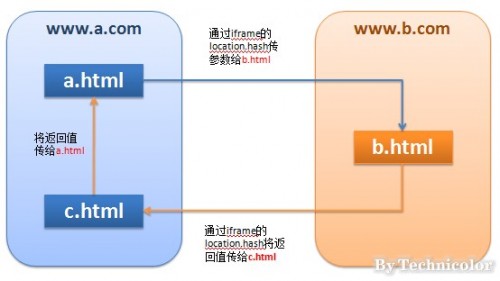
- 这个办法比较绕,但是可以解决完全跨域情况下的脚步置换问题。原理是利用location.hash来进行传值。www.a.com下的a.html想和www.b.com下的b.html通信(在a.html中动态创建一个b.html的iframe来发送请求)
- 但是由于“同源策略”的限制他们无法进行交流(b.html无法返回数据),于是就找个中间人:www.a.com下的c.html(注意是www.a.com下的)。
- b.html将数据传给c.html(b.html中创建c.html的iframe),由于c.html和a.html同源,于是可通过c.html将返回的数据传回给a.html,从而达到跨域的效果。
<script>
function startRequest(){
var ifr = document.createElement('iframe');
ifr.style.display = 'none';
ifr.src = 'http://www.b.com/b.html#sayHi'; //传递的location.hash
document.body.appendChild(ifr);
}
function checkHash() {
try {
var data = location.hash ? location.hash.substring(1) : '';
if (console.log) {
console.log('Now the data is '+data);
}
} catch(e) {};
}
setInterval(checkHash, 2000);
window.onload = startRequest;
</script>b.html代码如下:
<script>
function checkHash(){
var data = '';
//模拟一个简单的参数处理操作
switch(location.hash){
case '#sayHello': data = 'HelloWorld';break;
case '#sayHi': data = 'HiWorld';break;
default: break;
}
data && callBack('#'+data);
}
function callBack(hash){
// ie、chrome的安全机制无法修改parent.location.hash,所以要利用一个中间的www.a.com域下的代理iframe
var proxy = document.createElement('iframe');
proxy.style.display = 'none';
proxy.src = 'http://localhost:8088/proxy.html'+hash; // 注意该文件在"www.a.com"域下
document.body.appendChild(proxy);
}
window.onload = checkHash;
</script>由于两个页面不在同一个域下,IE、Chrome不允许修改parent.location.hash的值,所以要借助于a.com域名下的一个代理iframe,这里有一个a.com下的代理文件c.html。Firefox可以修改。
c.html代码如下:
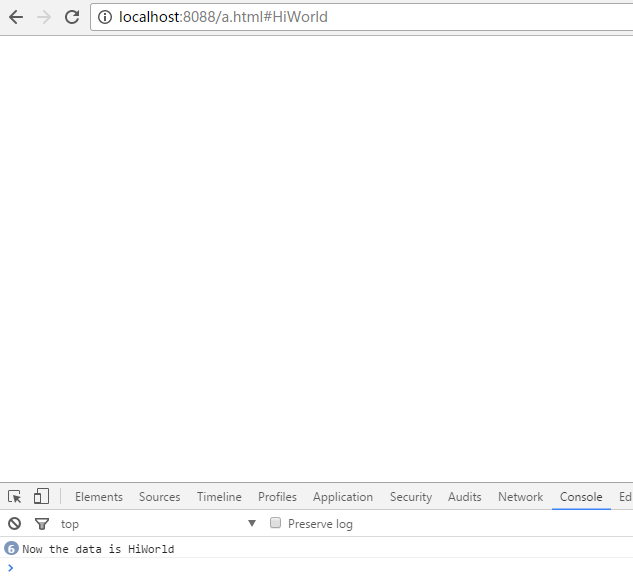
<script>parent.parent.location.hash = self.location.hash.substring(1); </script>直接访问a.html,a.html向b.html发送的消息为”sayHi”;b.html通过消息判断返回了”HiWorld”,并通过c.html改变了location.hash的值
8. flash URLLoader
flash有自己的一套安全策略,服务器可以通过crossdomain.xml文件来声明能被哪些域的SWF文件访问,SWF也可以通过API来确定自身能被哪些域的SWF加载。当跨域访问资源时,例如从域baidu.com请求域google.com上的数据,我们可以借助flash来发送HTTP请求。首先,修改域google.com上的crossdomain.xml(一般存放在根目录,如果没有需要手动创建) ,把baidu.com加入到白名单。其次,通过Flash URLLoader发送HTTP请求,最后,通过Flash API把响应结果传递给JavaScript。Flash URLLoader是一种很普遍的跨域解决方案,不过需要支持iOS的话,这个方案就不可行了。
小结
总的来说,常见的跨域方法如上述。在不同的业务场景下,各有适合的跨域方式。跨域解决了一些资源共享、信息交互的难题,但是有的跨域方式可能会带来安全问题,如jsonp可导致水坑攻击,``等标签会被用来进行xss或csrf攻击。所以,在应用跨域的场景,需要格外注意安全问题。